Introduction
In the digital age, innovation is the name of the game, and blockchain technology has emerged as a game-changer. This revolutionary technology has the potential to disrupt various industries, from finance to supply chain management, and beyond. But what exactly is blockchain, and why is it garnering so much attention? In this comprehensive introduction, we will delve into the world of blockchain, exploring its origins, core concepts, and the potential impact it could have on our lives.
The Origins of Blockchain
The concept of blockchain can be traced back to 1991 when cryptographers Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta proposed a system for securing digital timestamps. However, it wasn't until 2008 that the term "blockchain" was first used in a whitepaper by the elusive figure known as Satoshi Nakamoto. In this paper, Nakamoto described a peer-to-peer electronic cash system that relied on a decentralized ledger to record transactions, which would later become known as Bitcoin. The blockchain was the underlying technology that enabled this system to function without the need for a central authority.
Understanding the Blockchain Structure
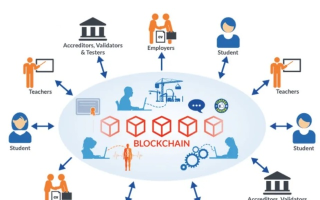
At its core, a blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that consists of a series of blocks, each containing a list of transactions. These blocks are linked together in a chronological order through cryptographic hashes, creating a chain. Here's a breakdown of the key components:
1、Blocks: Each block contains a group of transactions. Once a block is filled with transactions, it is closed and added to the chain. The process of adding a new block to the chain is called mining.
2、Transactions: These are the actions recorded on the blockchain, such as the transfer of cryptocurrency from one user to another.
3、Nodes: These are the computers that maintain a copy of the blockchain. They validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain.
4、Consensus Mechanism: This is the process by which nodes agree on the validity of transactions and the addition of new blocks. Proof of Work (used in Bitcoin) and Proof of Stake are common consensus mechanisms.
5、Cryptography: Blockchains use cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and control the creation of new units. Public and private keys are used to sign and verify transactions, ensuring that they can only be sent from the owner of the private key.

The Benefits of Blockchain Technology
1、Decentralization: By removing the need for a central authority, blockchains can reduce the risk of fraud and manipulation. They also allow for greater transparency and trust among participants.
2、Security: The use of cryptography and the immutable nature of the blockchain make it extremely difficult for hackers to alter the data once it has been recorded.
3、Transparency: All transactions on a blockchain are visible to everyone on the network, which can help in tracking and verifying the authenticity of transactions.
4、Efficiency: Blockchains can streamline processes by automating tasks and reducing the need for intermediaries, leading to cost savings and faster transactions.
5、Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted, ensuring a permanent and reliable record.
Blockchain Beyond Cryptocurrencies
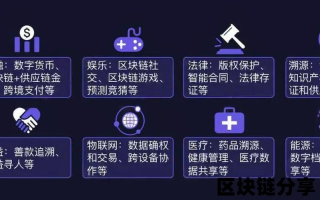
While blockchain technology was initially developed for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, its potential applications extend far beyond digital money. Here are a few examples:
1、Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can provide a transparent and tamper-proof record of the journey of goods, from production to delivery. This can help in tracking the authenticity of products and reducing fraud.
2、Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They can automatically execute when predetermined conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing efficiency.
3、Voting Systems: Blockchain can be used to create secure and transparent voting systems, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring that every vote is counted.
4、Healthcare: Blockchain can securely store and share patient data, ensuring privacy and improving the efficiency of healthcare systems.
5、Identity Verification: Blockchain can provide a secure and decentralized way to verify identities, reducing the risk of identity theft and simplifying the process of proving one's identity.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its potential, blockchain technology faces several challenges:
1、Scalability: As the number of transactions on a blockchain increases, the system can become slower and less efficient.
2、Energy Consumption: Some consensus mechanisms, like Proof of Work, require a significant amount of energy, raising environmental concerns.
3、Regulation: The decentralized nature of blockchain can make it difficult to regulate, which may lead to legal and compliance issues.
4、Adoption: For blockchain to reach its full potential, widespread adoption is necessary. This requires overcoming skepticism and educating the public about its benefits.
Despite these challenges, the future of blockchain looks promising. As the technology matures and solutions to these issues are developed, we can expect to see blockchain becoming an integral part of our digital infrastructure, transforming the way we conduct business and interact with the world.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is more than just the backbone of cryptocurrencies; it is a powerful tool with the potential to revolutionize various aspects of our lives. As we continue to explore its capabilities and overcome its challenges, the impact of blockchain on society could be as significant as the internet itself. It is an exciting time to be at the forefront of this technological revolution, and understanding the basics of blockchain is the first step in navigating this new digital landscape.