编写一个简单的区块链挖矿代码
```python
import hashlib
import time
class Block:
def __init__(self, index, timestamp, data, previous_hash):
self.index = index
self.timestamp = timestamp
self.data = data
self.previous_hash = previous_hash
self.nonce = 0
self.hash = self.calculate_hash()
def calculate_hash(self):
sha = hashlib.sha256()
sha.update((str(self.index) str(self.timestamp) str(self.data) str(self.nonce) str(self.previous_hash)).encode('utf8'))
return sha.hexdigest()
def mine_block(self, difficulty):
while self.hash[0:difficulty] != '0' * difficulty:
self.nonce = 1
self.hash = self.calculate_hash()
print("Block mined: ", self.hash)
class Blockchain:
def __init__(self):
self.chain = [self.create_genesis_block()]
self.difficulty = 4 难度系数,表示hash前几位必须为0
def create_genesis_block(self):
return Block(0, time.time(), "Genesis Block", "0")
def get_latest_block(self):
return self.chain[1]
def add_block(self, new_block):
new_block.previous_hash = self.get_latest_block().hash
new_block.mine_block(self.difficulty)
self.chain.append(new_block)
def is_chain_valid(self):
for i in range(1, len(self.chain)):
current_block = self.chain[i]
previous_block = self.chain[i 1]
if current_block.hash != current_block.calculate_hash():
return False
if current_block.previous_hash != previous_block.hash:
return False
return True
使用示例
blockchain = Blockchain()
print("Mining block 1...")
blockchain.add_block(Block(1, time.time(), {"amount": 4}, ""))
print("Mining block 2...")
blockchain.add_block(Block(2, time.time(), {"amount": 8}, ""))
print("Blockchain valid? ", blockchain.is_chain_valid())
```
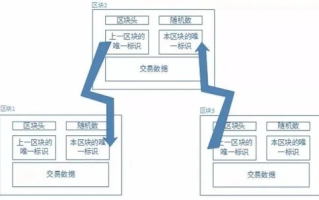
这个简单的区块链挖矿代码使用Python编写。它包括了区块和区块链类。每个区块都有一个索引、时间戳、数据、前一区块的哈希值和一个随机数(nonce),并通过SHA256算法计算自己的哈希值。挖矿过程是通过不断调整nonce值,直到找到一个哈希值前几位为0的值为止。难度系数表示哈希值前几位必须为0的个数,随着计算量的增加,难度也会增加。整个区块链通过链表形式连接起来,每个区块都包含前一区块的哈希值,确保了整个链的完整性。